testicular torsion lift test|testicular torsion signs on examination : white label Prehn's sign (named after urologist Douglas T. Prehn) is a medical diagnostic indicator that was once believed to help determine whether the presenting testicular pain is caused by acute epididymitis or from testicular torsion. Although elevation of the scrotum when differentiating epididymitis from testicular torsion is of clinical value, Prehn's sign has been shown to be inferior to Doppler ultrasound to rule out testicular torsion. WEBLoterias | CAIXA
{plog:ftitle_list}
Elisa chance e pipokinha fodame fodame fodame. Xxx-hd. Vídeos Relacionados. HD. 5 min. Elisa chance e outra mulher . HD. 11 min. Elisa chance gostosa . HD. 4 min. Gangbang Elisa chance . HD. 3 min. Elisa chance suruba . HD. 15 seconds. Elisa chance 2023 . HD. 7 min. Elisa chance e pamela . AD. 2 min. Quer ganhar R$7.000 agora? .
Prehn's sign (named after urologist Douglas T. Prehn) is a medical diagnostic indicator that was once believed to help determine whether the presenting testicular pain is caused by acute epididymitis or from testicular torsion. Although elevation of the scrotum when differentiating epididymitis from testicular torsion is of clinical value, Prehn's sign has been shown to be inferior to Doppler ultrasound to rule out testicular torsion. Testicular torsion is a clinical diagnosis, and patients typically present with severe acute unilateral scrotal pain, nausea, and vomiting. Physical examination may reveal a high-riding. Doctors often diagnose testicular torsion with a physical exam of the scrotum, testicles, abdomen and groin. Your doctor might also test your reflexes by lightly rubbing or .Individual clinical findings that best predict testicular torsion include nausea and vomiting, past trauma, a tender testicle, an abnormal testicular lie (i.e., elevated or transverse), and an.
Testicular torsion is a urologic emergency caused by the twisting of the testicle on the spermatic cord leading to constriction of the vascular supply, time-sensitive ischemia, . Testicular torsion occurs when the testicle rotates on the spermatic cord, which brings blood to the testicle from the abdomen. If the testicle rotates several times, blood flow to .
Diagnosis of testicular torsion is based on the finding of decreased or absent blood flow on the ipsilateral side. Treatment involves rapid restoration of blood flow to the affected testis. The.Diagnosis |. Treatment. Testicular torsion is the twisting of a testis on its spermatic cord so that the blood supply to the testis is blocked. Testicular torsion causes sudden, severe pain and later swelling of the affected testis. A doctor's .
crush test concrete
Testicular torsion is a twisting of the spermatic cord and its contents and is a surgical emergency affecting 3.8 per 100,000 males younger than 18 years annually. It accounts for 10% to 15% of
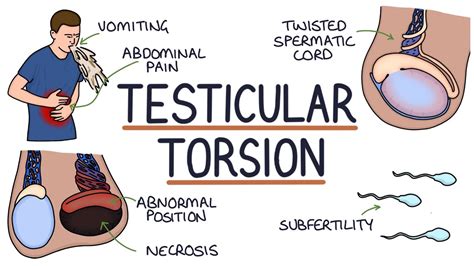
Testicular torsion is a medical emergency. Learn what causes your testicle to twist and why you need to treat this condition right away. . You might get one or more of these tests to diagnose . How common is testicular torsion? Testicular torsion occurs in teenage boys aged 13-18 years. This is found to happen in around 1 in 4,000 young men. Newborn babies and younger children sometimes develop this problem. It is uncommon over the age of 25 but does occur sometimes in older adults and can occur at any age. Ask the patient to lift their penis out of the way to allow you to closely inspect the scrotum and perineum for relevant clinical signs: Skin changes: warts . Prehn’s test is used to differentiate testicular pain caused by acute epididymitis and testicular torsion. The test involves elevating the testes to assess the impact on testicular pain.
The cremasteric reflex has been reported to be absent in 100% of cases of testicular torsion, making it a potentially useful sign in this diagnosis. However, a significant number of case reports and small case series exist, demonstrating that the test is not 100% specific, and the reflex can be present in cases of testicular torsion.
↑ Blaivas, M, et al. Emergency evaluation of patients presenting with acute scrotum using bedside ultrasonography. Academic Emergency Medicine. 2001; 8(1):90-93. ↑ Barbosa, JA, et al. Development of initial validation of a scoring system to diagnose testicular torsion in children. The Journal of Urology. 2013; 189:1853-8. ↑ Gordon J, Rifenburg RP. . Spermatic Cord . On physical exam, the scrotum is blue and firm with some erythema. Transillumination test is negative. Doppler ultrasound shows absent blood flow. The neonate is immediately sent to hospital for surgery. Introduction. . Testicular Torsion Renal - Testicular Torsion; Listen Now 15:31 min. 9/6/2021. 48 plays. 0.0 (0) This topic addresses the diagnostic evaluation and initial management of the acute scrotum in adults, which is typically due to testicular torsion, perineal necrotizing fasciitis (Fournier's gangrene), or acute epididymitis. This topic also addresses the clinical management of testicular torsion.
Depending on the circumstances, your doctor might do a testicular exam followed by a blood test, ultrasound or biopsy. Most changes in your testicles aren't caused by testicular cancer. A number of noncancerous conditions can cause changes in your testicles, such as a cyst, injury, infection, hernia and collection of fluid around the testicles . Acute scrotum pain is defined as “the constellation of new-onset pain, swelling, and/or tenderness of the intrascrotal contents.” Patients may describe the onset of symptoms as rapidly as occurring within minutes or up to 1 to 2 days, dependent on the etiology. The acute scrotum is an umbrella term that includes a wide variety of unique disease processes. Rapid .This video provides an overview of how to perform Prehn's test to elicit Prehn's sign in the context of testicular pain when testicular torsion is suspected..
Testicular torsion occurs when the spermatic cord becomes twisted. This causes a restriction in blood flow to the testes, severe pain, and possibly permanent damage. . Tests that can be used to .
Testicular torsion repair: This surgery, typically performed by a urological surgeon aims to restore the blood supply to the testicles.; Orchiectomy: Most testicular cancers also involve surgery, removing both the tumor and testicle itself.The removal of a testicle is called orchiectomy.; Surgical debridement: This is the removal of damaged or dead tissue, such as . Consider the diagnosis of testicular torsion in all patients with acute testicular pain; Testicular torsion is a surgical emergency that requires immediate urologic consultation to increase the rate of tissue salvage. History, physical examination and ultrasound are all flawed in making the diagnosis. The gold standard is surgical exploration
Testicular Torsion What is testicular torsion? Testicular torsion (tes-TICK-yoo-ler TOR-shun) . like a urine test or an ultrasound of the scrotum. If you do have testicular torsion, you will Testicular torsion: Acute onset of pain with a high-riding testis, swelling, very tender: Varicocele: Usually asymptomatic or dull ache, unilateral “bag of worms” in the scrotum:
A diagnosis of testicular torsion should be suspected in any person presenting with acute scrotal pain and/or swelling, before other causes are considered.. Ask about:. Any scrotal pain — the location (including unilateral or bilateral), nature, radiation to surrounding structures, speed of onset, duration, severity, exacerbating factors (such as activity or positional changes).Testicular torsion is the twisting of a testis on its spermatic cord so that the blood supply to the testis is blocked. Testicular torsion causes sudden, severe pain and later swelling of the affected testis. A doctor's examination and sometimes ultrasonography are needed for testicular torsion diagnosis. Treatment is to untwist the spermatic cord.
testicular torsion signs on examination
What is a testicular self-exam? A testicular self-exam (TSE) is a step-by-step method to check the appearance and feel of your testicles (testes). It’s important to be familiar with your testicles — and your body in general — so you can more easily notice changes or potential problems, including testicular cancer.A healthcare provider may also conduct a testicular exam during .Testicular torsion is the twisting of a testis on its spermatic cord so that the blood supply to the testis is blocked. Testicular torsion causes sudden, severe pain and later swelling of the affected testis. A doctor's examination and sometimes ultrasonography are needed for testicular torsion diagnosis. Treatment is to untwist the spermatic cord.Inspect from the front but also ensure you lift the scrotum to inspect posteriorly: Skin: erythema, rashes, excoriations, scars, . Prehn’s test: if testicular pain is relieved by elevating the testes, suspect epididymitis; if not, suspect testicular torsion . if not, suspect testicular torsion; Cremasteric reflex: stroke inside of leg and . Although testicular torsion is rare, it is an emergency. Sudden testicular pain demands an immediate trip to the emergency room. If treatment is delayed, the testicle can die.
crush test does he like me
Testicular torsion is an emergency condition. It happens when the spermatic cord, which provides blood flow to the testicle, rotates and becomes twisted. The twisting cuts off the testicle's blood supply and causes sudden pain and swelling. Testicular torsion requires surgery right away to save the .
Testicular torsion in young boys and teen boys occurs when the testicles are not completely attached in the scrotum. This lets the testicles move more freely and twist. . He may also have tests, such as an ultrasound. This is a painless imaging test that uses sound waves to see the scrotum and testicles and check blood flow. Testicular torsion occurs when the testicle rotates around the spermatic cord, which provides blood to the scrotum (a bag of skin that contains the testicles). Testicular torsion typically affects adolescents, although it can occur at all ages, including newborns and older adults. . Additional diagnostic methods include urine tests to exclude . Testicular torsion: In cases of testicular torsion, a condition where the testicle twists upon its blood supply, the cremasteric reflex is typically absent or reduced on the affected side. This finding can aid in the diagnosis of testicular torsion and .
testicular torsion signs and symptoms
Testicular torsion is when the spermatic cord above your testicle twists, cutting off blood flow to your testicle. Testicular torsion can happen at any age, but it most often happens to boys ages 12 to 18 or babies. Without blood supply, the tissue of your testicle can die in a few hours . See a doctor right away if you think you have .
testicular torsion prognosis
Resultado da Stations of the Cross. Christ the King Church. Please join us on Fridays in Lent to pray. The Stations of the Cross 6:30pm - Beginning Friday, Feb. 16. St. Stephen Church. Please join us on Fridays for 12pm Stations of the Cross in the church. We are also open for self-guided outdoor stations on Fridays .
testicular torsion lift test|testicular torsion signs on examination